A fracture of the tibia is a serious injury that affects one of the most important bones in the human body. The tibia bone, located in the lower part of the leg, Plays a key role in load transfer and stabilization during walking. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, treatment and rehabilitation to better understand the importance of proper post-injury management.
Fracture of the tibia - causes
As for the tibia, Fracture most often occurs as a result of high force trauma, such as car accidents, falls from heights or direct blows to the leg. In athletes, fractures can be The effect of overloads, sprains or severe collisions during physical activity. For elderly people whose bone structure is weakened by osteoporosis, even a minor injury can lead to a fracture. There are different types of fractures:
- simple fracture of the tibia - Where the bone breaks in one place, without displacement of the fragments;
- multifracture fracture of the tibia - is characterized by the breakdown of the bone into many fragments, which makes the healing process much more difficult;
- open fracture of the tibia and fibula - requiring immediate surgical intervention due to the risk of infection.
A special form is an open fracture of the tibia and fibula, in which the skin is broken and the bone is exposed. This type bone fracture is more complicated, requires intensive surgical treatment and carries a higher risk of infection. In the case of multifracture injuries, where the bone splits into several fragments, treatment is even more challenging and time-consuming.
Fracture of the tibia - symptoms
A fracture of the tibia is an injury with a symptoms are usually clear and difficult to miss. Symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the fracture, but in most cases include intense pain and difficulty moving. Early recognition of these symptoms is key to prompt treatment. Typical symptoms include:
- severe pain at the site of injury, aggravated by an attempt to move or load the limb, which can prevent even minimal movement of the leg;
- swelling, bruising and deformity of the leg, often resulting from damage to the surrounding soft tissues and blood vessels;
- mobility difficulties, and in the case of severe fractures - the complete inability to stand on the damaged leg, which requires immediate relief of the limb;
- leg shortening or unnatural positioning, especially in the case of multifracture fractures, which can cause additional complications associated with displacement of bone fragments.
Symptoms such as an open wound, bleeding or palpable displacement of bone fragments may indicate an open fracture of the tibia and fibula, which poses a risk of infection and requires urgent medical intervention. For such injuries, it is crucial to quickly implement surgical treatment and thoroughly clean the wound to prevent complications. It is worth remembering that ignoring symptoms can lead to permanent mobility limitations, so any suspicious situation should be consulted with a doctor.
Fracture of the tibia - methods of treatment
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the injury. For simple fractures, the following are used immobilization with a plaster or orthosis. More complicated cases, such as a multifracture fracture of the tibia, require surgery, during which plates, screws or intramedullary nails are used to fuse the fragments. For open fractures, the priority is to prevent infection and thoroughly clean the wound. Surgical treatment also includes bone stabilization and closure of damaged tissues.
The healing time of a tibia fracture is on average 8 to 16 weeks, but full recovery may take much longer, especially if surgery was required. In such cases, it is also important to adapt the loads to the patient's condition and gradually increase the intensity of the exercises during rehabilitation to promote proper bone fusion and restore full function to the leg.
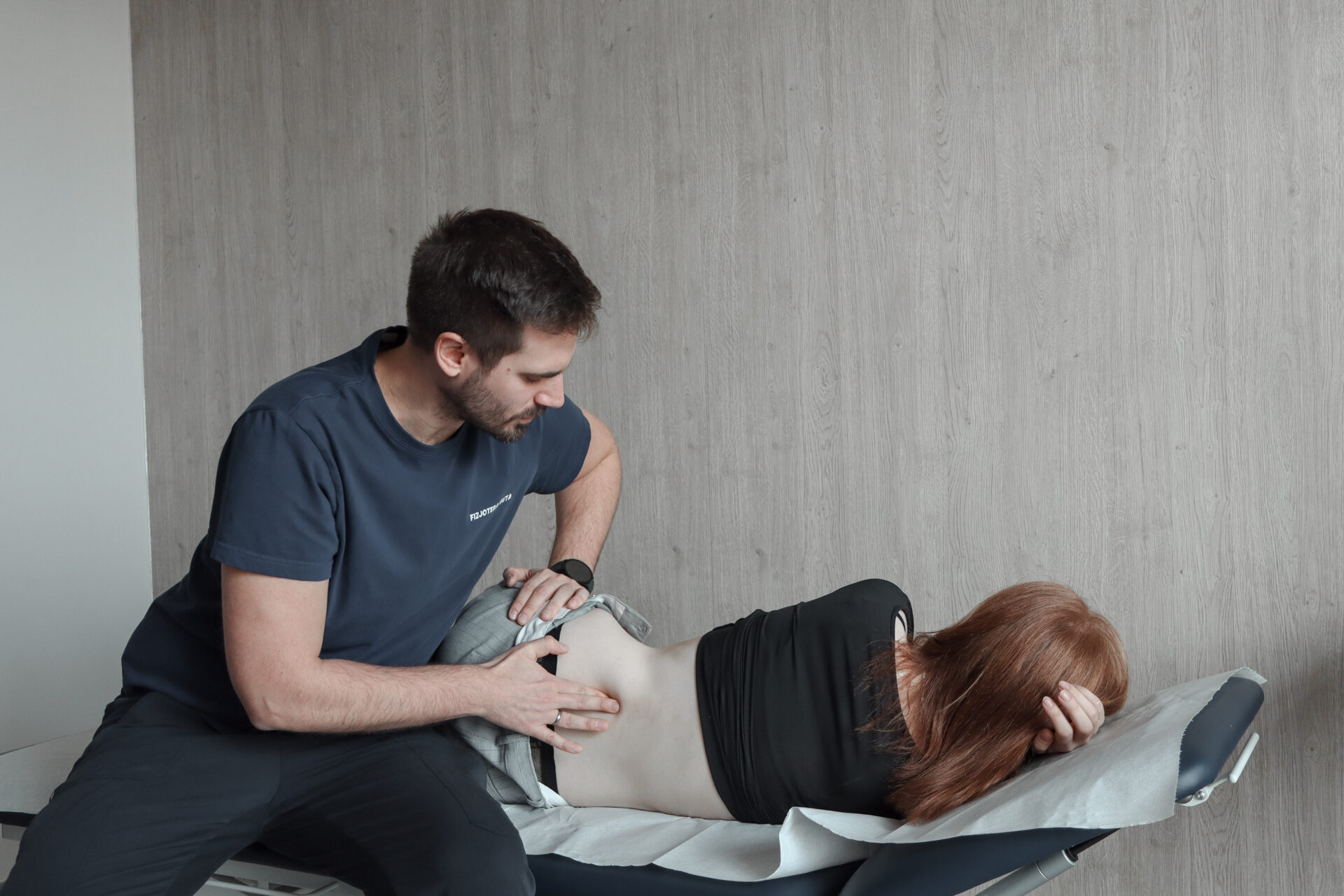
Rehabilitation after tibia and fibula fracture
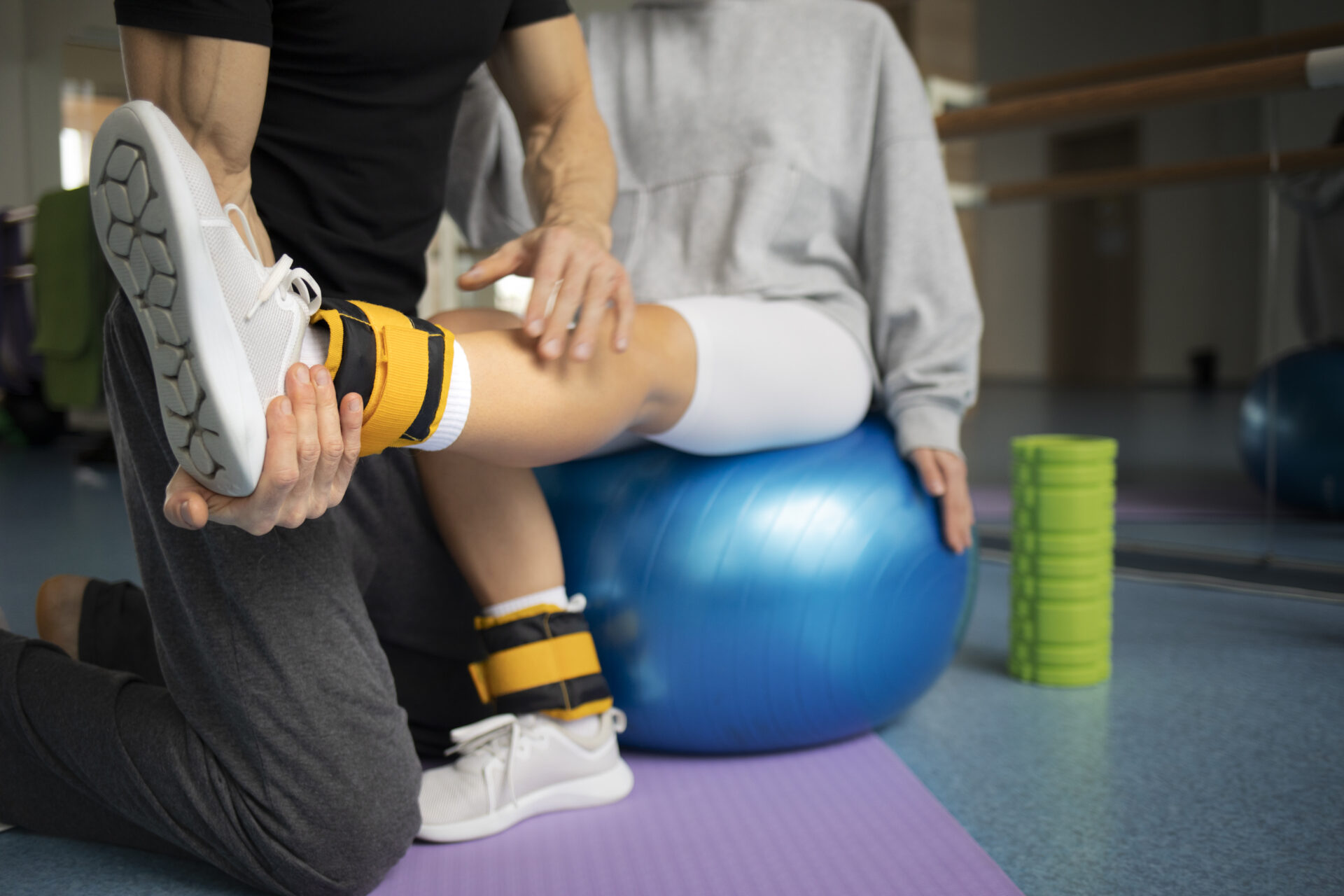
Rehabilitation after a tibia fracture is a key step in the recovery process. Initially, the patient performs gentle exercises aimed at improving circulation and reducing swelling. As healing progresses, more advanced exercises are introduced to strengthen muscles and improve range of motion. Regular work on stability and balance avoids future injuries and strengthens the functionality of the limb.
Modern methods, such as physical therapy, help relieve pain and speed up the recovery process. The use of ultrasound therapy, laser therapy or electrotherapy promotes tissue recovery and reduces inflammation. Modern rehabilitation after a tibia fracture also includes the use of advanced devices, such as rehabilitation robots and dynamic exercise platforms. They increase the effectiveness of therapy and shorten the time to return to full function. It is also worth considering individually tailored home exercises, which support the rehabilitation carried out at the center.
How to deal with challenges after a fracture?
Patients who have suffered a tibia fracture often struggle with movement limitations, pain and concerns about full recovery. Regular exercise, attention to a proper diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and support of specialists is the key to success. It is also important to gradually increase the load on the leg, as recommended by the doctor and physiotherapist, to avoid re-injury.
Equally important is the use of modern rehabilitation methods that promote tissue regeneration, reduce pain and improve range of motion. Long-term cooperation with a physiotherapist, an individually tailored rehabilitation plan and regularity in exercise allow for a faster return to full fitness. Taking care of mental health and motivation also play an important role in supporting the recovery process and helping patients overcome daily challenges.
Summary
A tibia fracture is an injury that requires a comprehensive approach - from appropriate surgical treatment, to long-term rehabilitation, to psychological support for the patient. Prompt medical intervention and Systematic rehabilitation after tibia and fibula fracture, which allows you to regain fitness and quality of life. Thanks to modern methods such as physical therapy and individually tailored rehabilitation programs, Patients can successfully return to full activity. If you are looking for professional care, visit our Neuroport rehabilitation center.